STATIONARY BIKE
The Upright Stationary Bike is designed to simulate the range of motion of a regular bike that you ride outdoors. Bike riding is a great low impact, and therefore a knee-friendly, way of toning your legs whilst achieving a terrific aerobic workout. In addition to general cardio workouts, this piece of equipment is also ideal for anyone seeking to take things up a notch and incorporate high-intensity training into their workouts.
Skill Level: Beginner
Training: Cardiovascular
Equipment: Upright Stationary Bike
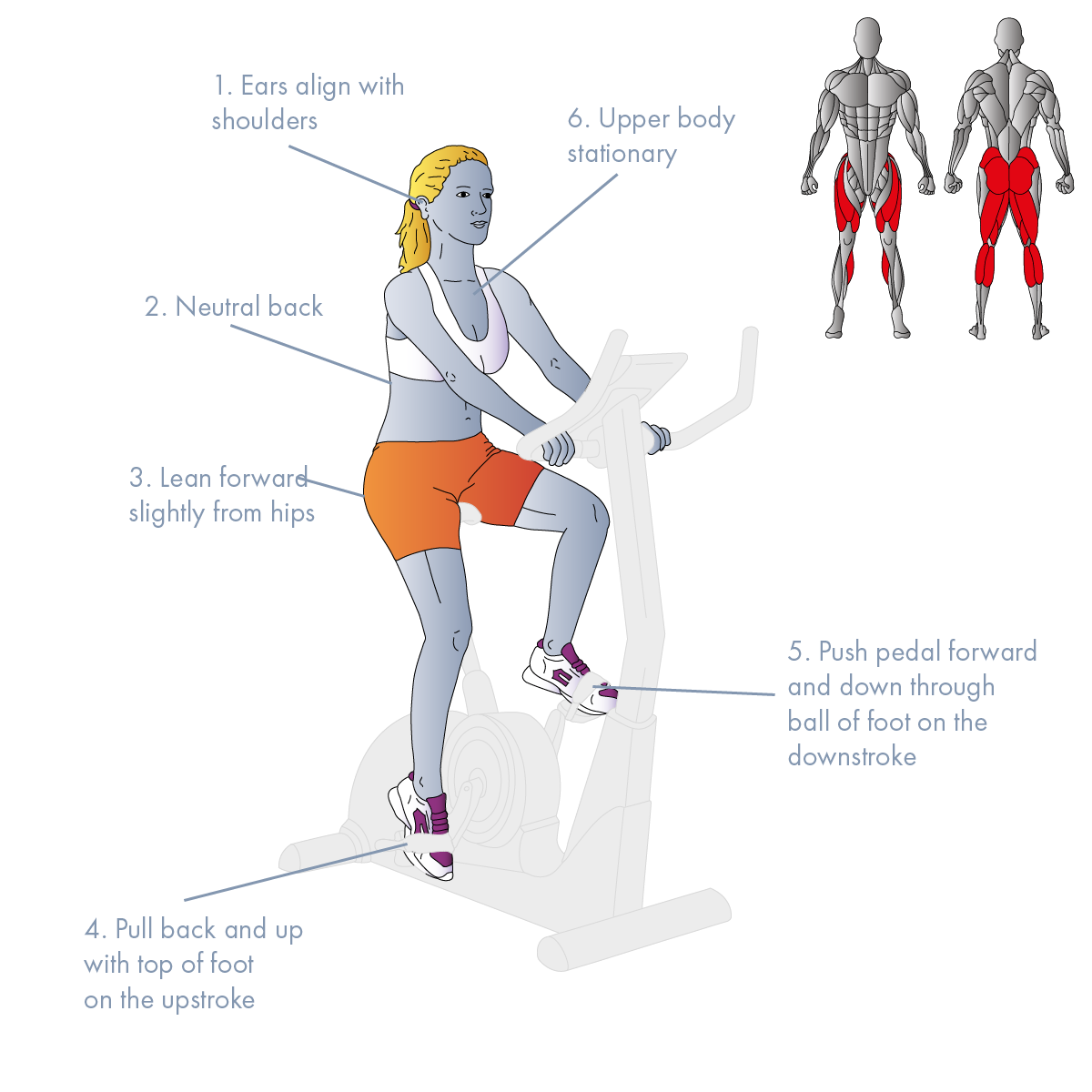
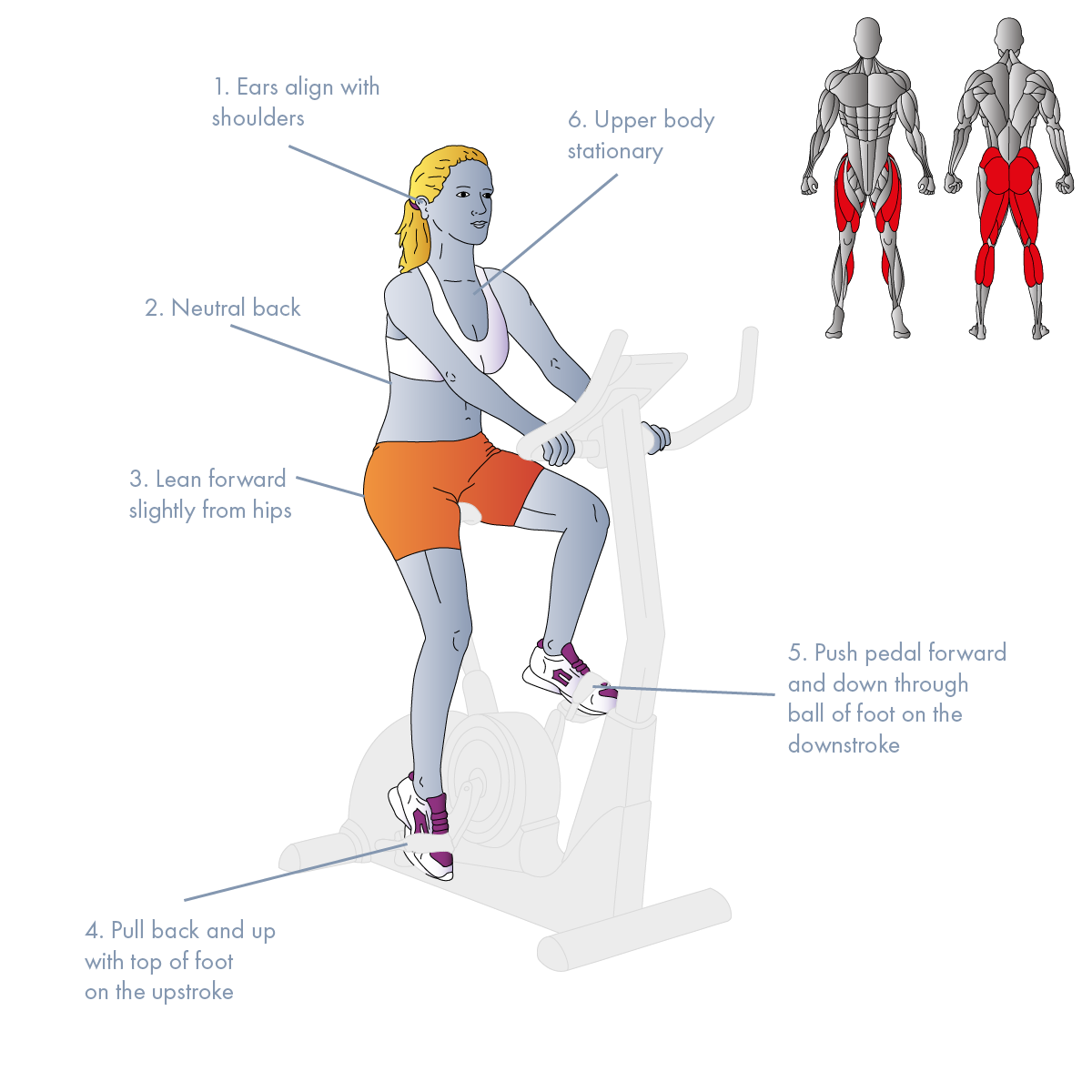
1° Muscles: Gluteals, Hip Flexors (Iliacus, Psoas), Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Soleus, Gastrocnemius
SET-UP
- ADJUST THE SEAT: Stand next to the bike and adjust the height of the seat to align with the top of your hips, specifically the intersection between your femur and hips. To test whether this height is right for you, sit on the bike and place your feet on the pedals. When the pedals are at the bottom of the pedal stroke, without leaning to the side and your foot flat, your legs should be almost, but not quite, straight - aim for a 5-15 degree bend. If the seat can also be adjusted horizontally, the front of the seat should align with the center pin of the pedal when set at 3 o’clock.
- ADJUST THE HANDLEBARS: As a rough rule of thumb, the optimal height for the handlebars should match the height of the saddle. However, novices, individuals with back issues, and those who are pregnant may opt for a slightly higher height. Nevertheless, overall the handlebar height should allow you to hold it securely in a comfortable position with your arms almost, but not fully, extended.
- FAMILIARIZE YOURSELF WITH THE CONSOLE: the number of levels (resistance) varies considerably between different models from anything between 12 – 40, so level 4 may feel considerably different between machines with different ranges.
- FOOT PLACEMENT: Position each foot on the pedals so that they are directly over the center spindle. Adjust the pedal straps so that your feet are snug, but not so tight that they cut off circulation.
EXECUTION
- POSTURE: Maintain a neutral back, keeping your chest up and your shoulders drawn back and down. Lean forward slightly from your hips, not your lower back. Your ears should vertically align with your shoulders, and your stomach should be drawn in.
- FOOT ACTION: Your feet should not only push the pedals forward and down through the ball of your foot on the downstroke but also they should pull back and up with the top of your foot on the upstroke.
- PEDAL STROKE: Pedal smoothly without much movement of your upper body.
- CADENCE: This refers to the number of revolutions you make per minute (rpm). Most individuals should aim for something between 70 – 90 rpm for a general cardio workout, though higher rates of 90-130 rpm are appropriate for high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
- If you feel any strain in your hips or they rock at the bottom of the pedal stroke the seat might be set too high.
- If your knees feel crunched at the top of the pedal stroke the seat might be set too high.
- Whilst setting the height of the handlebars lower than the height of the saddle is advantageous when riding on the road or track to make you more aerodynamic, this is clearly not necessary on a stationary bike. Raising the handlebars to equal or exceed the height of the saddle will set you up into a more upright position and may make for a more comfortable workout.
- Avoid peddling through your toes to minimize cramps in your feet and calf muscles.
- If you find yourself bouncing up and down, reduce the speed at which you are pedaling whilst simultaneously increasing the resistance.
- To avoid back and neck pain, avoid rounding your back and instead aim to maintain a neutral back.
- Stationary bike riding is not a full-body workout; your upper body should contribute little to no effort to this exercise. Therefore, you should not rock your torso wildly from side to side, grit your teeth, or clench the handlebars, during this exercise. If you find yourself doing so, reduce the resistance and/or cadence.
- Recumbent Bike
- Cross Trainer
RELATED EXERCISES
Top